- Home
- betapharm-co
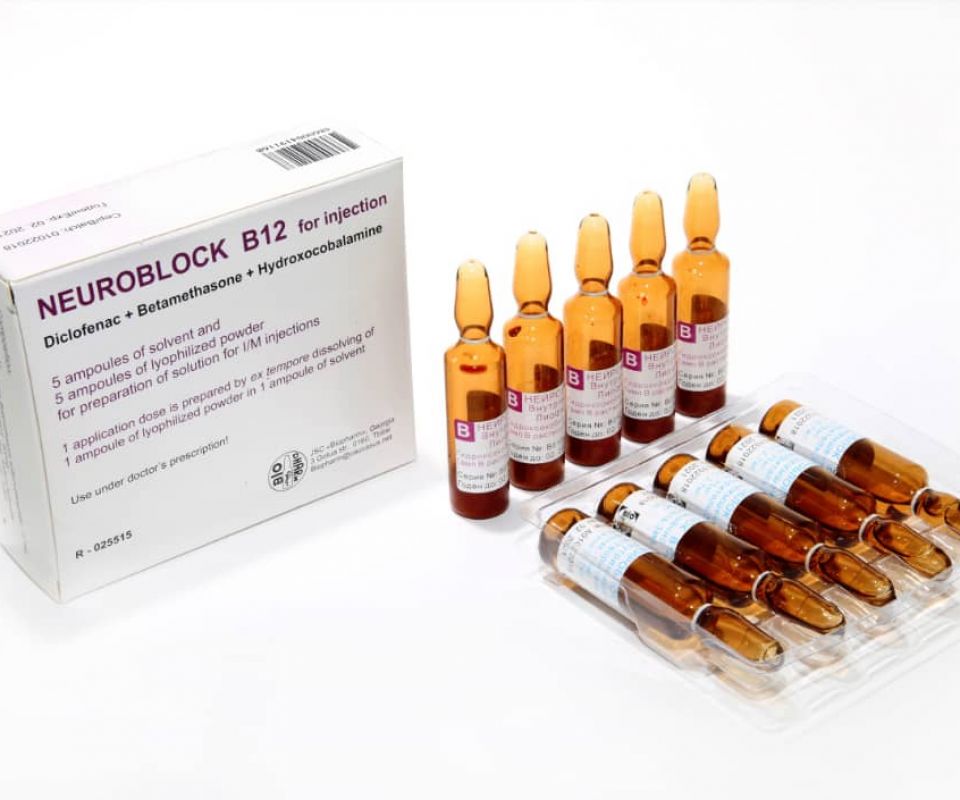
- NEUROBLOCK B12
NEUROBLOCK B12
The drug is a complex of three active moieties that determine its pharmacological properties.
INN: Betamethasone Complex + diclofenac + vitamin В12
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Anti-inflammatory, analgesic. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
ATC-code: M01АВ55
Drug form and formulation:
Solvent (Ampoule A) and dried cake (Ampoule B) for extempore preparation of solution for intramuscular injection. 1 dose is prepared by dissolving the contents of 1 ampoule B in 1 ampoule A.
Each solvent ampoule (Amp A) contains:
Active moiety: Diclofenac sodium – 75.0 mg; Betamethasone Sodium Phosphate – 2.7 mg.
Excipients: Benzyl alcohol – 120.0 mg; Propylene glycol – 600.0 mg; Mannitol – 18.0 mg; Sodium metabisulfite – 9.0 mg; Sodium hydroxide q.s. pH 8.4; Water for injection to a volume of 3 ml.
Each ampoule (Amp B) of the dried cake contains:
Active moiety: Hydroxocobalamin acetate – 10.0 mg.
Excipients: Mannitol – 35.0 mg.
Pharmacological properties:
The drug is a complex of three active moieties that determine its pharmacological properties.
Pharmacodynamics:
Diclofenac – a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, whose mode of action is similar to that of NSAIDs, is not fully understood. It is able to inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins – this is part of its pharmacological action.
Betamethasone – a glucocorticoid that suppresses inflammation through several mechanisms: it inhibits the formation of various factors of the inflammatory reaction, including vasoactive and chemotactic factors. It reduces the secretion of lipophilic and ‘proteolytic enzymes, reduces the release of leukocytes to the damaged areas and reduces fibrosis; finally, it also affects the number and immune responses that are dependent on lymphocytes.
Vitamin B12 – essential for cell growth and reproduction. Its derivative, methylcobalamin, is required for the formation of methionine and S-adenosylmethionine from homocysteine. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause irreversible damage to the nervous system, with progressive neuron tumor, demyelonization, and death resulting from nervous state.
Pharmacokinetics:
Diclofenac – excreted by metabolism in the liver. It is excreted in urine (65%) and bile (35%), as metabolites combined with sulfur or glucuronide. No changes in pharmacokinetics were found in geriatrics or in patients with hepatic or renal failure.
Betamethasone – circulates in a bound state with plasma proteins (64%), and its half-life is 5.6 hours.
Vitamin B12 – It is mainly distributed in the cells of the hepatic parenchyma, which make up its main storage site.
Indications for use:
Acute inflammatory rheumatism (rheumatic fever); rheumatoid arthritis; lumbar ischalgia (sciatica); polyradiculoneuropathy; neuralgia in the cervical spine; osteoarthrosis; myositis; injuries (domestic and sports)
Dosage and Administration:
The drug is administered intramuscularly to adults.
1 dose of the drug is prepared by dissolving 1 ampoule of dried cake (amp B) in the contents of 1 ampoule of solvent (amp A).
1 or 2 doses of the drug are administered per day and night at a 12-hour interval. The dose for each patient is determined individually.
The drug is injected deep into the clunis with a long needle, each subsequent injection into another clunis. After injection, at the injection site, a circular massage is recommended for 3-5 minutes.
Contraindications:
– hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
– active gastroduodenal ulcer, gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation;
– severe renal or hepatic insufficiency;
– decompensated heart failure, severe hypertension;
– systemic mycosis;
– active tuberculosis;
– arthragra;
– osteoporosis;
– diabetes mellitus;
– hypersensitivity to aspirin and other NSAIDs;
– A, B and non-A non-B hepatitis and other viral diseases;
– treatment with anticoagulants;
Pregnancy and lactation:
During pregnancy and lactation, the administration of the drug is contraindicated.
Pediatric use:
The administration of the drug in children is contraindicated.
Side effects :
Neuroblock B12 can cause the following systemic adverse reactions:
Gastrointestinal tract: epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal distension, gastric bleeding, gastric or duodenal ulcer with or without hemorrhage or perforation;
CNS: convulsions, increased intracranial pressure, dizziness, migraine and drowsiness;
Cardiovascular system: Arterial hypertension, heart failure and flutter;
Liver: sometimes, an increase in transaminase and rarely hepatitis with or without jaundice;
Kidneys: isolated cases of acute renal failure, hematuria and proteuria;
Hematopoietic system: Isolated cases of leukopenia, hemolytic anemia and agranulocytosis;
Musculoskeletal system: muscle weakness, steroid myopathy, loss of muscle mass, osteoporosis, compression fractures of the spine, necrosis of the femoral head and / or pathological fracture of long bones;
Skin: sometimes, erythema and skin rash. Rarely urticaria. Delayed scarring of wounds, tenderness of the skin, petechiae and ecchymosis, blotch of the face. Hyperpigmentation or hypochromatism, skin and subcutaneous atrophy, abscess;
Endocrine system: menstrual irregularities, pituitary basophilia, adrenal insufficiency, especially in cases of injuries, surgery, systemic diseases. Decreased carbohydrate tolerance and increased need for insulin and oral sugar-lowering drugs in diabetic patients;
Water-electrolytic disturbances: sodium retention, edema, potassium loss and hypokalemic alkalosis;
Sense body: subcapsular cataract, increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma, pain in bright light and tinnitus;
Metabolism: negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolism.
Drug interactions:
The combined administration of Neuroblock B12 with other NSAIDs can lead to adverse effects.
In patients taking oral anticoagulants, the drug is recommended for administration with strict monitoring of blood coagulation.
Neuroblock B12 can inhibit the pharmacological action of diuretics, and also increase the delay in potassium due to inhibition of diuretics.
The drug is prescribed with caution 24 hours or after a dose of methotrexate, as this can increase its level in the blood and its toxicity.
The combined administration of Neuroblock B12 and lithium salts can increase the level of latter in the blood without signs of overdose.
The neuroblock B12 contains a steroid (betamethasone), and, accordingly, when it is simultaneously administered with: erythromycin, astemizole, bepridil, halofantrine, pentamidine, terfenadine, sultopride, vincamine, the risk of flutter, ventricular fibrillation increases (hypokalemia, brachycardia and lengthening the QT interval increases the risk of developing this arrhythmia) .
Associations that require careful administration:
Antiarrhythmic drugs that lead to the development of flutter, ventricular fibrillation, such as: amiodarone, brithelia, disopyramide, quinidine, sotalol. Digitals increase the risk of toxic effects in case of hypokalemia. Substances that lead to hypokalemia with i/v administration are amphotericin B, thiazide diuretics and catoterics.
Acetylsalicylic acid: corticosteroids increase the excretion of salicylate. Therefore, there is a risk of an overdose of salicylate after interruption of treatment with corticosteroids. Adjusting the dose of salicylate after discontinuation of corticosteroid treatment is recommended.
Oral anticoagulants and parenteral heparin: in these cases, it is recommended to strengthen patient monitoring, since corticosteroids increase the risk of hemorrhage. This effect may be noticeable when high doses of corticosteroids are taken for periods longer than ten days.
Insulin, metformin, sulfonamides that lower blood glucose: in these cases, it is recommended to strengthen monitoring of the patient’s glucose level and adjust the dose of antidiabetic drugs during and after treatment with corticosteroids.
Isoniazid: The level of isoniazid in the blood decreases when isoniazid is administered together with corticosteroids. In these cases, clinical and microbiological monitoring is recommended.
Phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, carbamazepine, rifabutin, rifampicin: all of them are enzyme inducers that reduce the effectiveness of corticosteroids. Therefore, it is recommended to adjust the dose of the drug during and after treatment with these medicines.
Associations to consider:
Antihypertensive drugs: corticosteroids reduce their therapeutic effects.
Alpha interferon: corticosteroids may interrupt its therapeutic effect.
Vaccines with attenuated microbes: there is a risk of developing systemic diseases that can ultimately be fatal. The risk will be greater in patients previously immunosuppressed, as a consequence of the underlying disease. Inactive microbial vaccines are preferred.
Special warnings:
Neuroblock B12 (contains diclofenac), should be used with caution in patients with renal, cardiac or hepatic disorders and in patients who have undergone serious surgery or reduced blood volume, Diclofenac may exacerbate the state in patients with liver porphyria, and may also exacerbate the state in patients who suffer from bronchial asthma.
When taking the drug, control is necessary in patients with a duodenal ulcer, ulcerative colitis or Crohn disease.
Patients with coagulation disorders or those taking oral anticoagulants should also be controlled.
Neuroblock B12 (contains betamethasone) should be administered with caution in patients with diverticulitis, intestinal anastomosis, gastric ulcer, ulcerative colitis, abscesses or other purulent diseases, hypertension, osteoporosis and myasthenia gravis.
With prolonged therapy with the drug, it is necessary to check the blood formula, kidney and liver function.
Overdose:
Symptoms: A typical clinical picture of an overdose does not exist. The following symptoms of an overdose are possible: vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding, diarrhea, dizziness, tinnitus, convulsions. In case of severe poisoning, severe renal failure or liver damage is possible.
Treatment: Depending on which component of the drug has caused acute poisoning, the treatment measures are as follows:
Diclofenac – primarily a general supportive measure and symptomatic treatment.
Betamethasone – an overdose does not cause the development of life-threatening conditions, but requires strict medical supervision. It is necessary to control the electrolytes in the blood (serum) and urine, strict control of the sodium / potassium balance in the body, when an imbalance is observed, appropriate therapy is carried out.
When convulsions occur, diazepam or other benzodiazepines are prescribed intravenously. Hemorrhage or stomach ulcer should be taken into account. Vitamin K is prescribed in case of hypoprothrombinemia.
Storage conditions:
Keep out of the reach of children, protected from light, at a temperature of + 15 ° C to + 25 ° C.
Note: In case of violation of the temperature regime of storage (excessive cooling) in solvent ampoules (ampA), reversible crystal formation is possible, which should disappear when the solution is heated to a temperature of 35 ° – 45 ° C. If the crystals do not disappear, use of a solvent is unacceptable!
Shelf life: 3 years.
Dispensing rules: By prescription